- level of all operating fluids;
- condition of all hoses and pipelines;
- air filter;
- engine cooling systems;
- engine lubrication systems;
- condition of drive belts;
- spark plug status (glow plugs);
- AB charging;
- AB state.
The most carefully check the power supply, ignition and battery charging systems. This section of the manual contains only a part of the scope of checks, the main material is presented in the relevant sections of the manual.
Oil level control
Check the oil level in the following order:
- warm up the engine by making a trip of 25-30 km at high speed;
- after stopping, wait at least 5 minutes for the oil to drain into the oil pan and visually check the engine for oil leaks;
- check the oil level with a clean dipstick (fig 1.122). The difference between the marks on the dipstick is about 1 liter of oil;
Warning! The oil level must be between the marks, otherwise engine malfunctions may occur. Only high quality oil should be poured into the engine.
- check the oil in the engine: if the oil has become milky or drops of water can be seen in it, this indicates a violation of the tightness of the cylinder head gasket or a crack in the head or cylinder block;
- check the cleanliness of the oil as follows: remove the dipstick and pull it between your thumb and forefinger. If dirt or metal particles are found, change the oil;
- restore the oil level through the filler neck on the cylinder head cover.
Normal oil consumption should not exceed 0.5 liters per 1000 kilometers. High oil consumption indicates either an oil leak or increased wear on the valve stem seals and piston rings.
Search for an oil leak in the following order:
- 1) if the engine is contaminated with oil and its consumption is increased, check the places of possible oil leaks, for which pay attention to the following points of connection of engine parts:
- gasket by opening the filler cap;
- crankcase ventilation hoses;
- cylinder head cover gasket;
- cylinder head gasket;
- oil filter gasket;
- drain plug sealing ring;
- landing of the oil pressure sensor;
- oil pan seal;
- front and rear crankshaft and camshaft seals;
- 2) isolate the generator with plastic wrap;
- 3) wash the engine with shampoo and water;
- 4) sprinkle the places of possible leakage with talc or ground chalk;
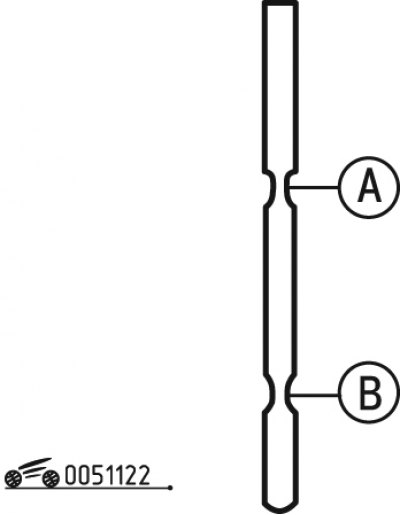
Pic. 1.122. Checking the oil level with an oil dipstick: A - maximum oil level; B - minimum oil level
- 5) check the oil level with a dipstick and top it up. The oil level must be between the two marks (see fig. 1.122). Add oil up to the top mark.
Coolant level control
All models of the Peugeot 206 series are equipped with an overpressure compensation type cooling system. The expansion tank is located in the engine compartment, mounted on the front wall and connected to it with a hose. As the engine temperature rises during operation, the expanding coolant fills the reservoir. When the engine cools down, the liquid returns back to the cooling system, which ensures that a constant level is maintained. Antifreeze is used as a coolant - a solution of ethylene glycol (40%) in distilled water (60%).
Warnings!
- 1. Antifreeze is toxic - if it enters the body, it causes poisoning. In addition, it destroys the paintwork.
- 2. It is forbidden to remove the filler cap until the engine has completely cooled down (up to ambient temperature).
Check the coolant level in the following order:
- 1) check the coolant level. On a cold engine, the fluid level should be above the mark «MIN» on the tank. As the engine warms up, the level should approach the mark «MAX». If this is not the case, let the engine cool down and remove the cap from the expansion tank;
- 2) if you need to add a small amount of liquid, you can use distilled water;
- 3) with a systematic drop in the level of the coolant, determine the location of the leak in the cooling system;
- 4) inspect the engine cooling jacket, radiator, hoses, expansion tank cap, plugs, coolant pump;
- 5) check the tightness of the cap of the filler neck of the expansion tank;
- 6) check the purity of the antifreeze, if the color changes (brown or rusty) flush the cooling system and replace the antifreeze. It is recommended to replace antifreeze at 120 thousand km or every five years;
- 7) check the tightness of the entire system.
Brake Fluid Level Control
Warning! Brake fluid is toxic. Avoid contact with skin and eyes; in addition, brake fluid destroys the paintwork of the body. Brake fluid is hygroscopic (absorbs moisture from the environment), so it can not be stored in an open container. Mixing different types of fluids such as DOT3 or DOT4 with DOT5 can cause brake system failure.
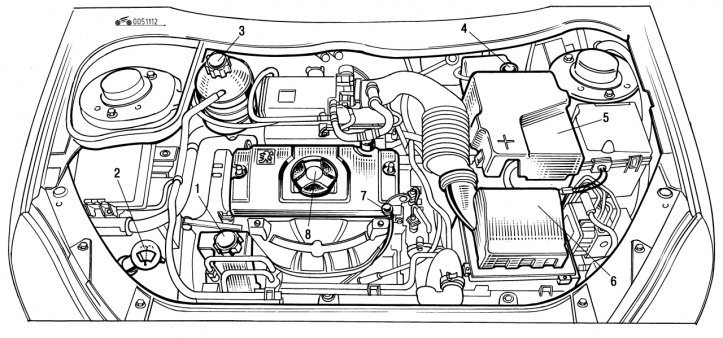
Pic. 1.112. Engine compartment (petrol engine 1.1 and 1.4 l): 1 - hydraulic booster reservoir; 2 - windshield and headlight washer reservoir; 3 - the neck of the expansion tank of the cooling system; 4 - the neck of the brake fluid reservoir; 5 - battery; 6 - air filter; 7 - oil dipstick; 8 - oil filler neck
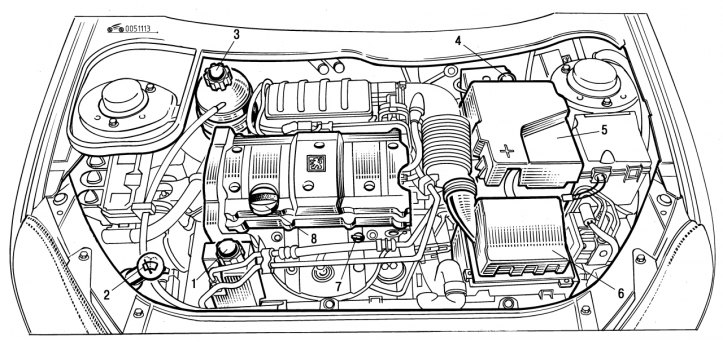
Pic. 1.113. Engine compartment (gasoline engine 1.6 l 16V): 1 - hydraulic booster reservoir; 2 - windshield and headlight washer reservoir; 3 - the neck of the expansion tank of the cooling system; 4 - the neck of the brake fluid reservoir; 5 - battery; 6 - air filter; 7 - oil dipstick; 8 - oil filler neck
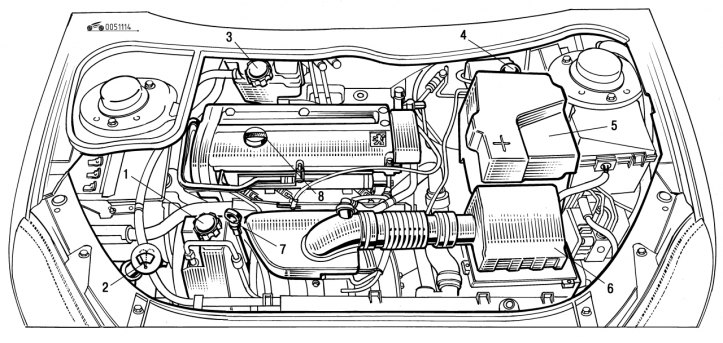
Pic. 1.114. Engine compartment (petrol engine 2.0 l 16V): 1 - hydraulic booster reservoir; 2 - windshield and headlight washer reservoir; 3 - the neck of the expansion tank of the cooling system; 4 - the neck of the brake fluid reservoir; 5 - battery; 6 - air filter; 7 - oil dipstick; 8 - oil filler neck
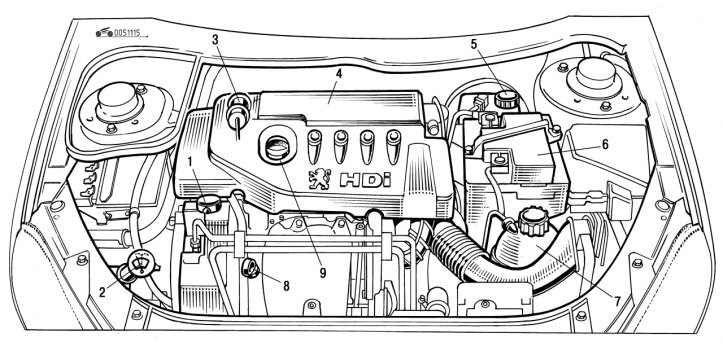
Pic. 1.115. Engine compartment (diesel engine 1.4 l HDI): 1 - hydraulic booster reservoir; 2 - windshield and headlight washer reservoir; 3 - fuel priming pump; 4 - air filter; 5 - the neck of the brake fluid reservoir; 6 - battery; 7 - expansion tank of the cooling system; 8 - oil dipstick; 9 - oil filler neck
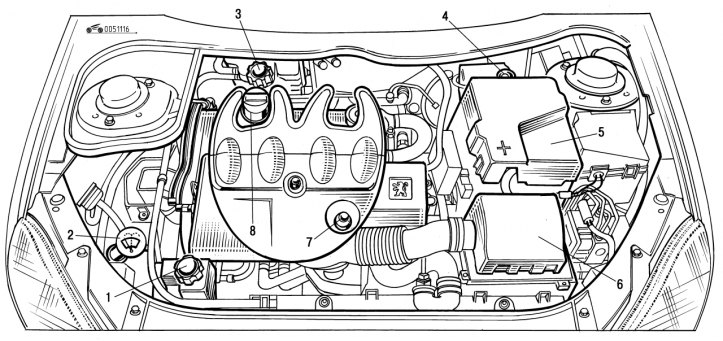
Pic. 1.116. Engine compartment (diesel engine 1.9 l): 1 - hydraulic booster reservoir; 2 - windshield and headlight washer reservoir; 3 - the neck of the expansion tank of the cooling system; 4 - the neck of the brake fluid reservoir; 5 - battery; 6 - air filter; 7 - oil dipstick; 8 - oil filler neck
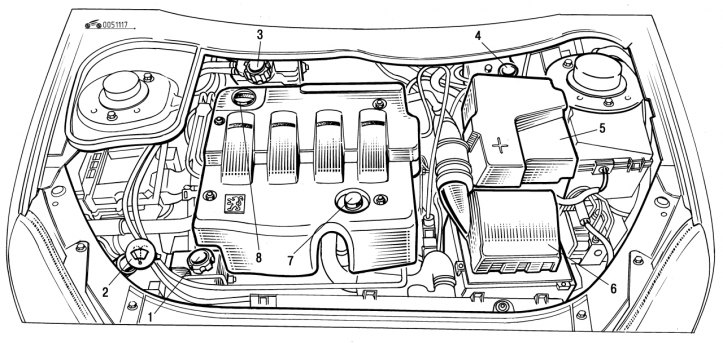
Pic. 1.117. Engine compartment (diesel engine 2.0 l, HDI): 1 - hydraulic booster reservoir; 2 - windshield and headlight washer reservoir; 3 - the neck of the expansion tank of the cooling system; 4 - the neck of the brake fluid reservoir; 5 - battery; 6 - air filter; 7 - oil dipstick; 8 - oil filler neck
Reservoir 4 (see fig. 1.112, 1.113, 1.114, 1.116, 1.117) or 5 (see fig.1.115) for brake fluid located in the engine compartment on the left side (from the driver's side). The vent hole in the screw plug must always be kept clean (open). In a transparent tank, it is easy to control the liquid level. When the level drops below the mark «DANGER» indicator lights up in the instrument cluster.
The fluid level in the closed tank must be between the marks «MAX» And «DANGER».
The brake fluid level may drop slightly due to worn brake pads. A significant decrease in the level of brake fluid indicates a leak from the system - stop driving the vehicle and immediately determine the location of the leak.
While visually inspecting the liquid level in the tank, check the function of the contacts of the level control float mechanism.
Wheels and tires
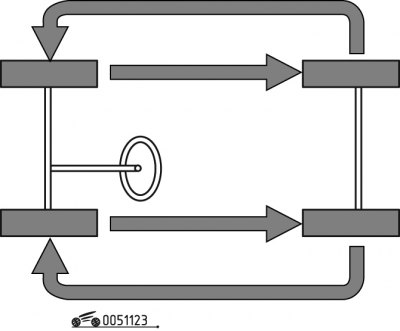
Pic. 1.123. Tire swap pattern
Change the tires on the car at least every 5000 km or when signs of uneven tread wear appear. The permutation scheme is shown in fig. 1.123. Carry out work on a raised and securely fastened vehicle.
The proposed scheme allows not to change the direction of tire rotation. Changing the direction of rotation leads to their intense wear.
After changing the wheels, check the air pressure in the tires and the tightness of the wheel bolts with a torque wrench. Tightening torque for wheel bolts 85 Nm (8.5 kgf·m).
It is recommended to periodically check the tightness of the wheel bolts every 1000 km.
Note. When changing tires and wheels on a vehicle with a satellite navigation system, recalibrate the system.
Tire condition check
On cars of the Peugeot 206 series, depending on the model, various tires and wheels are installed. All discs have so-called humps, which are a belt pressed on the rim of the disc that prevents movement (disruption) tubeless tire off the rim when the car is turning sharply.
Tires and wheels require regular inspection of their condition. On tires, first check the condition of the inflation valve and tread wear.
All tires are equipped with a built-in wear indicator in the form of control strips around the circumference, which are exposed when the tread depth decreases to 1.6 mm, after which the tires are considered worn. The optimal tire tread depth is 2.0 mm or more.
Check tire wear in several places at the same time, since tire wear depends on many factors:
- the condition of the road surface;
- tire pressure;
- driving style;
- atmospheric conditions;
- suspension condition;
- wheel balancing;
- front wheel alignment angles.
The location of the wear indicators is indicated on the side - «TWI» (Tread wear indicator) and sign «S». Performance of winter tires («M+S») on snow, mud and slush, it decreases already at a tread depth of less than 4 mm.
Wheel balancing
Serial wheels are balanced at the factory - the vehicle manufacturer. Balancing is necessary to eliminate the uneven distribution of masses and inaccuracies in the manufacture of parts.
Imbalance of the wheels leads to shaking, vibration of the steering wheel, damage to the suspension joints and shock absorbers. Vibration manifests itself in a certain range.
The wheels must be balanced every 20 thousand km of the car run and after each repair, which can cause a redistribution of masses on the wheels.
Tire care
Tire care comes down to the following rules and recommendations:
- do not wash tires with a jet of water or steam under pressure;
- do not allow the tire to come into contact with oil or grease;
- store tires in a dark, dry and cool place;
- store the wheels in a horizontal, suspended state;
- before removing the wheel from the car, increase the pressure in it by 20-50 kPa;
- install winter tires on your wheels;
- when installing new tires, run them in for the first 300 km, observing all precautions, especially in ice and rain, without exceeding the established speed;
- for driving on snow and ice, install snow chains only on the drive wheels, do not install chains on 17-inch wheels;
- the speed of the car with the chains installed must not exceed 50 km/h.
Winter operation of diesel engine
During winter operation of a diesel engine at low temperatures (below -150 С) one has to face the problem of an increase in the viscosity of diesel fuel and the precipitation of paraffin compounds. The problem is closely related to the quality of diesel fuel, especially its winter grade. To improve the performance of summer diesel fuel in winter, it is necessary to add special additives to it. This prevents the release of paraffin.
If the engine does not start:
- remove the fuel filter and heat it in a bath of water or replace it with a new one;
- put the car in a warm room (garage, workshop);
- spray the supply system with hot water.
Warning It is strictly forbidden to use open fire to heat the diesel engine power supply system.
