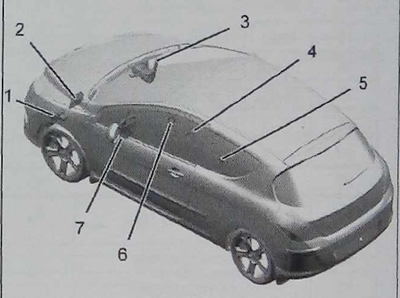
Location of CAN IS ECU

The CAN IS network connects control units related to the movement of the vehicle, such as the brake system!, gearbox or engine.
Data transfer rate 500 Kbps (High Speed).
The CAN IS network is a network of many blocks, where each of them constantly transmits information for all other blocks.
Each ECU processes its own information.
The transmission of messages over the network occurs periodically, except for messages that are random in nature. The CAN IS network has a device that allows communication when at least two control units are included in it.
Engine control ECU (1320) and switching unit (BSI 1) are the only computers that have terminating resistance.
To enable network communication, the engine control ECU (1320) and switching unit (BSI 1) should always be online.
Features of the CAN IS network:
- some control units are connected in a line that is activated by a command from a remote control (RDC), which allows preliminary «to wake» control units;
- diagnostic line K.
Note. A break in the CAN High or CAN Low wire makes network communication impossible.
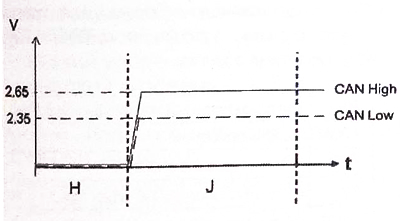
Designations:
- «H» — CAN network in standby mode;
- «J» — CAN network in operating mode;
- «V» - volt;
- «T» - time.
The CAN interconnection network is characterized by two average operating voltages:
- Can High - 2.65V;
- CAN Low - 2.35 V.
The CAN network is operational at CAN IS High + CAN IS Low = 5V.
Note. The voltage values shown are average values.
Nominal curves for CAN network (oscilloscope readings)
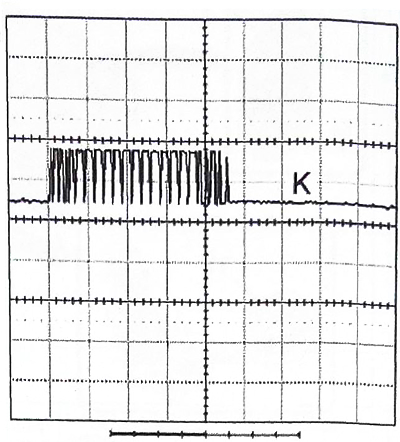 | 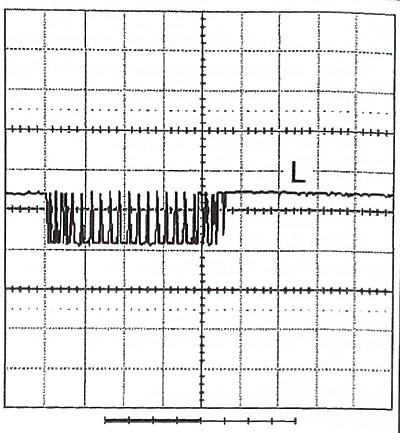 |
- «TO»: CAN High;
- «L»: CAN IS Low.
Voltage: 1 V.
Time: 100 m/s.
Test conditions:
- the engine is not running;
- ignition is on.
Results: observe a DC component of about 2.5 volts and a series of alternating pulses with an amplitude of 1 V, representing information transmitted over the CAN network.
The CAN Low signal is reversed from the CAN High signal.
