Elements of an automatic transmission
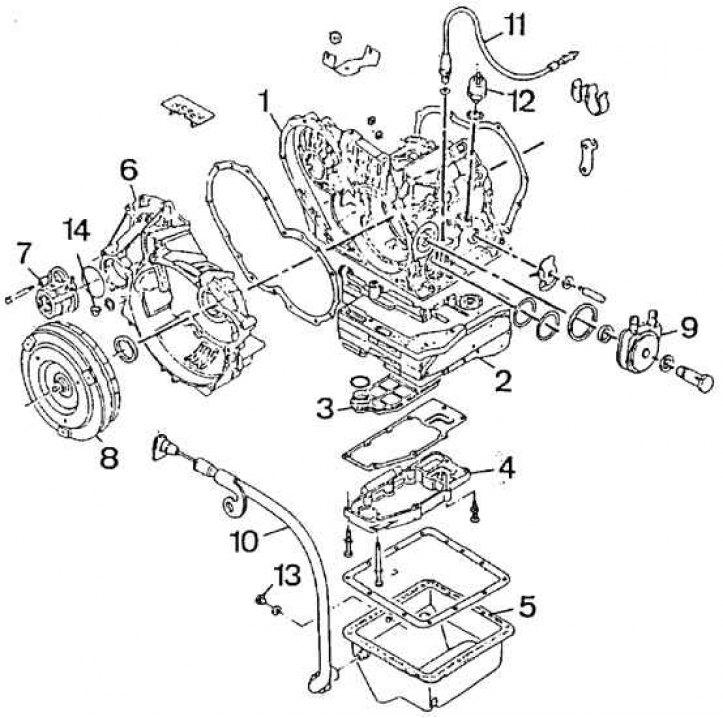
1 – case of an automatic transmission; 2 – control servomotor; 3 - filter; 4 – filter cover; 5 - oil pan; 6 – crankcase hydrokinetic transmission; 7 - differential bearing housing; 8 - hydrokinetic transmission; 9 - heat exchanger coolant / oil; 10 - oil level indicator; 11 - cable for forced downshifting ("kick-down"); 12 – the switch of lanterns of a backing; 13 - drain oil plug; 14 – a drain oil stopper of differential
External automatic transmission components
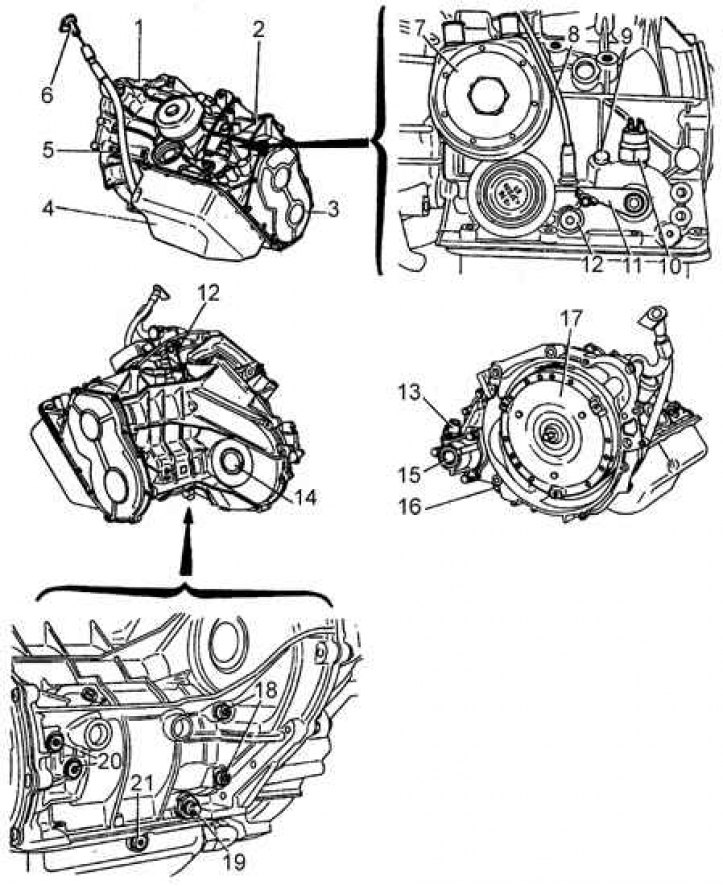
1 - torque converter housing; 2 - main crankcase; 3 - end cap; 4 - pallet; 5 - dipstick tube for measuring the oil level; 6 - dipstick for measuring the oil level; 7 - heat exchanger; 8 - cable for forced downshifting; 9 - breather; 10 - starter / reverse lamp switch; 11 - selector lever; 12 - eye; 13 - speedometer drive; 14 – the left exit of a transmission; 15 – the right exit of a transmission; 16 - drain plug; 17 - torque converter; 18 - bolts of the driven shaft bearing; 19 - brake band regulator; 20 - pressure check; 21 - drain plug
The drive consists of the following units: hydrokinetic transmission, gearbox, centrifugal regulator.
The hydrokinetic transmission consists of a pump, a turbine and a guide vane.
The gearbox primarily consists of:
- planetary gear, which allows you to get four forward gears and one reverse gear;
- hydraulic control servomotor providing automatic gear change control;
- a gear oil pump constantly driven by the hydrokinetic transmission pump, feeding the hydraulic control servo pump and hydrokinetic transmission, and providing lubrication to the planetary gear; limiting the maximum pressure provides an overflow valve.
The centrifugal governor is driven by an intermediate shaft; directly under the influence of the speed of the driven wheels, the centrifugal force acts on the weights, which change the speed signal into a pressure signal through flow throttling: this is the pressure "analyzed" inside the control servomotor and determines the gear change.
Kinematic diagram of an automatic transmission
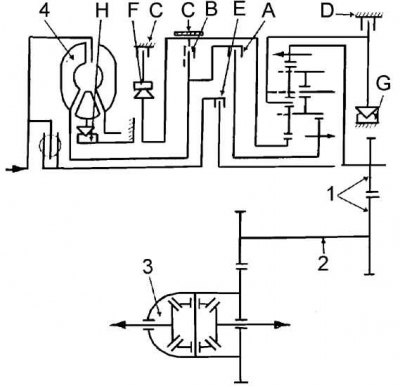
The gearbox contains:
- planetary gear;
- three multi-plate clutches (A, B and E), each driven by a hydraulic piston;
- three unidirectional clutches (F,G and H);
- one gear train at the output of the planetary gear, transmitting thrust to the intermediate shaft (2), which drives the differential (3);
- hydrokinetic transmission (4) at the input of the gearbox, which connects the engine to the gearbox;
- main gear and differential.
The assembly of mechanical elements is controlled by a hydraulic servomotor located at the bottom of the gearbox.
