Typical bearing defects
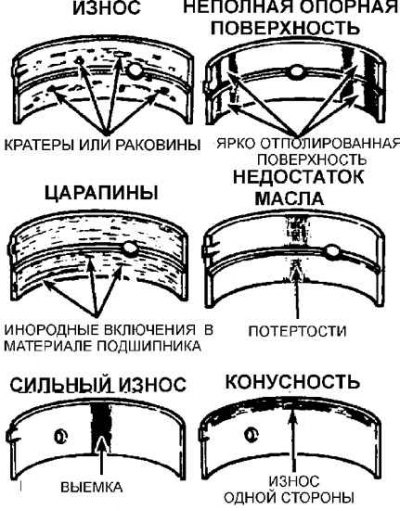
1. Even though the main and connecting rod bearings should be replaced when the engine is overhauled, they must be carefully inspected as they can provide valuable information regarding the condition of the engine.
2. Bearing failure can be due to lack of lubrication, the presence of dirt or other foreign matter, motor overload, or corrosion. Regardless of the cause of the bearing failure, the cause of the bearing failure must be corrected before the motor is reassembled.
3. When inspecting the bearings, remove them and lay them out in the same order as they were installed on the engine. This will identify the appropriate crankshaft journal and facilitate troubleshooting.
4. Foreign particles can enter the engine in various ways. Metal particles can be found in engine oil as a result of normal engine wear. Fine particles along with the engine oil can enter the bearings and are easily embedded in the soft bearing material. Large particles entering the bearing will scratch the bearing or crankshaft journal. The best way to prevent bearing failure from this cause is to thoroughly clean all internal surfaces of the motor and keep them clean when reassembling the motor. Frequent and regular oil and filter changes are also recommended.
5. Insufficient lubrication of the crankshaft journals can be caused by many different causes such as high oil temperatures, engine overload and oil leaks.
6. The way you drive your car also has an impact on bearing life. A fully open throttle at low engine speeds creates a high load on the bearings and extrusion of the oil film from the contact zone. These loads lead to cracks in the working part of the bearing, which weakens the bearing and can lead to separation of the anti-friction layer from the steel base.
7. Short distance driving results in corrosion of the bearings as a result of the motor not reaching a stabilized operating temperature that removes water vapor and corrosive gases. These vapors and gases, condensing in engine oil, form acid and sediment. Acid, along with engine oil, gets to the bearings, and bearing corrosion begins.
8. Incorrect selection of bearings during engine assembly also leads to bearing failure. Preloaded bearings leave insufficient bearing running clearance resulting in a reduced or no oil layer for lubrication.
