Removing
The replacement of pistons and connecting rods can only be carried out on a dismantled engine with a disconnected gearbox.
All pistons have two compression rings and one oil scraper ring. Piston rings are marked, which must face up when the ring is installed (see illustration 22.0).
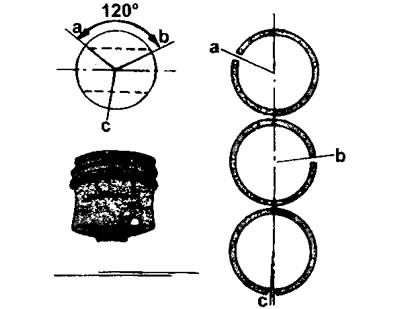
22.0 Piston rings and their location on the piston
a - top compression ring
b - middle compression ring
c - lower (oil scraper) ring
In diesel engines, the cylinder pistons must protrude slightly from the surface of the cylinder block, so the cylinder head gaskets have different thicknesses.
No special tools are required to disassemble the pistons and connecting rods. The connecting rod and piston group for all engines is the same. Pistons in different engine models differ only in size (see illustration 22.0a).
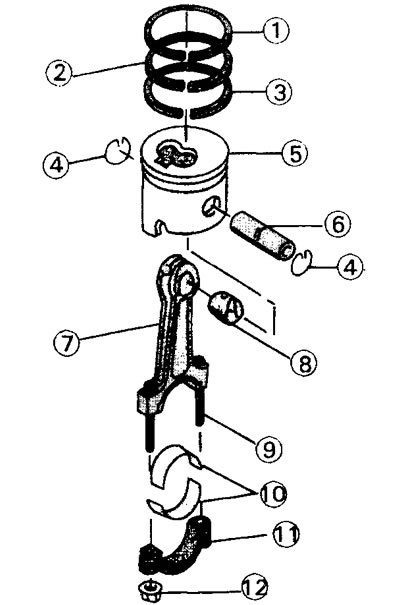
22.0a Parts of the connecting rod and piston group
1 - top compression ring
2 - middle compression ring
3 - oil scraper ring
4 - piston pin retaining ring
5 - piston
6 - piston pin
7 - connecting rod
8 - connecting rod bushing
9 - connecting rod bolt
10 - connecting rod bearing shells
11 - connecting rod cover
12 - connecting rod cover fastening nut
1. Remove the piston rings in order to shine using piston ring pliers. If the same rings are re-installed, they should also be marked in order to put them in their original places. In the absence of pliers for installing piston rings, the latter are removed by placing metal plates under both ends of the rings.
2. Remove thrust rings from piston pin. To remove them, you need a small screwdriver, because. thrust rings do not have a ledge. The thrust rings can also be removed with a hook by bending a piece of wire as needed.
3. Place the piston with connecting rod on a suitable support and knock out the piston pin. If finger «is sitting» tightly, then the piston together with the connecting rod can be heated in boiling water.
Attention! Disconnect the piston and connecting rod is performed only in cases where replacement of the piston or connecting rod is necessary.
4. Carefully inspect all parts. If there are scuffs, scratches or wear, they must be replaced.
Assembly
It is assumed that all parts are checked and faulty replaced.
5. Check for twisting and deflection of the connecting rods on a connecting rod tester. This is best done in a workshop, as bent or even twisted connecting rods will cause the engine to malfunction.
6. Lubricate all parts with engine oil.
7. Arrange the pistons and connecting rods in the order of assembly, that is, the cavity of the combustion chamber in the bottom of the piston and the protrusion under the connecting rod bearing shell should be located on the same side, as shown in (illustrations 22.7.)
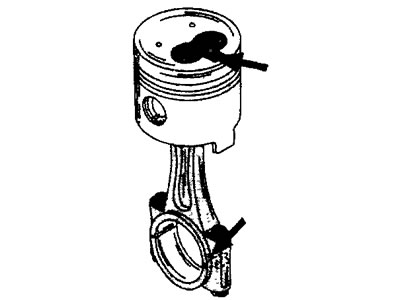
22.7 The cavity of the combustion chamber in the bottom of the piston and the protrusion under the connecting rod bearing shell must be located on the same side
8. Install the connecting rod and piston so that the connecting rod bore and piston bore match. Install a piston pin circlip on one side of the piston and make sure it is firmly seated in the bore.
9. Insert a piston pin from the opposite side of the piston and hammer it in until it stops. If necessary, use a plastic mallet. Then install the second retaining ring.
10. Check the stroke of the connecting rod on the piston pin. To do this, while holding the piston in your hands, move the connecting rod in different directions. The connecting rod should move easily.
11. Install piston rings on the pistons (see illustration 22.0). Remember that the factory marking of piston rings or the inscription «TOR» should point upwards, and the joint of the oil scraper ring should be in line with the hole for the piston pin. joints (locks) compression rings must be offset by 120°from the junction of the oil scraper ring (see illustration 22.0). Lubricate the piston rings liberally with engine oil.
12. Lubricate the piston with engine oil and insert it into the appropriate cylinder liner. A special mandrel is required to compress the piston rings when installing the piston. Install the tie-down mandrel around the piston so that the top edge of the piston protrudes 4-5 mm from under it. This ensures that the piston is evenly positioned in the cylinder bore.
13. Install the connecting rod bearing caps (see relevant chapter).
