In early 1997, the installation of upgraded 1.9-liter engines began, designated XUD9 BTF / W2 (D8B) and XUD9 BTF/L3. W2 indicates the level of harmful substances in the exhaust gas, which has been brought into line with the legislation for passenger cars. The XUD9 BTF/W2 engines do not have an EGR valve.
As for the XUD9 BTF / L3 engines, this is, in fact, the same XUD9 TF engine, but equipped with a Bosch VP20 fuel injection system that works with an electronically controlled injection pump. The VP20 electronic fuel injection system control unit regulates injection timing and fuel delivery, exhaust gas recirculation, monitors the preheat relay, altitude corrector, idle speed increase, air conditioning, engine speed sensor and self-diagnosis system. This engine is equipped with a different gearbox, designated ML5T.
The 2.1 liter engine of the XUD1 family 1 is designated XUD11BTE/L3 (R8S) and is equipped with the EPIC fuel injection system developed by Lucas. L3 also indicates the degree of content of harmful substances in the exhaust gas. The new engine injection pump has fuel control valves, a fuel injection adjustment solenoid valve, a fuel cut-off valve and various sensors, including a fuel temperature sensor, a distributor rotor and cam position sensor. The injectors of the cylinders are of the same design, but differ in the shape of the body. The reason for this is the installation of the needle lift sensor of the nozzle of cylinder No. 4. Like the 1.9 liter engine, this engine is also equipped with a gas turbine supercharger.
To dismantle the injection pump on all types of engines, it is necessary to remove the toothed belt.
Attention! Since 1997, the control lamp for the level of condensate in the fuel filter has not been installed on the instrument panel. In this regard, it is recommended to drain the condensate every 10,000 km.
The injection pump is located on the left side of the cylinder block and is driven by a toothed timing belt. The electric fuel cut-off valve installed on the high-pressure fuel pump is designed to force the fuel supply to stop when the engine is turned off.
The fuel system of all engines consists of the following components: fuel tank, fuel heating unit, air filter, injection pump and four nozzles.
Fuel filter and fuel heating unit
Fuel filtration and heating are an integral function of the fuel injection system. The fuel is heated by the coolant passing through the heating block at the outlet pipe. The thermal valve installed on the heating unit regulates the volume of heated fuel. Fuel heating depends on the outside temperature. When the air temperature drops below 15°C, the thermal valve opens, freeing the channel «A» (see illustrations 1.0 and 1.0a).
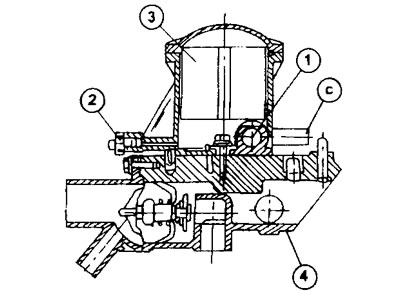
1.0 Fuel filter and fuel heating block in section
1 - thermal valve
2 - vent plug
3 - fuel filter
4 - coolant outlet pipe
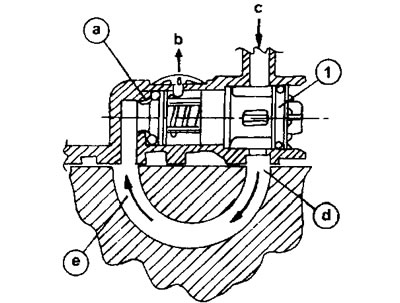
1.0a Scheme of movement and fuel heating
a - thermal valve
c - inlet on the fuel heating unit
d - fuel circulation channel in the heating unit, washed by hot coolant
e and b - outlets on the heating block leading to the fuel filter
At outdoor temperatures of 15-30°C, the thermal valve is only ajar and only a small part of the fuel enters the heating unit. The main fuel flow is directed directly from «With» V «b».
The fuel circulation circuit is equipped with an automatic ventilation valve.
Exhaust gas recirculation system
All engines are equipped with this system, regardless of whether a catalyst is installed or not. The exhaust gas recirculation system reduces the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere by directing part of the exhaust gas to the intake manifold (see illustration 1.0b).
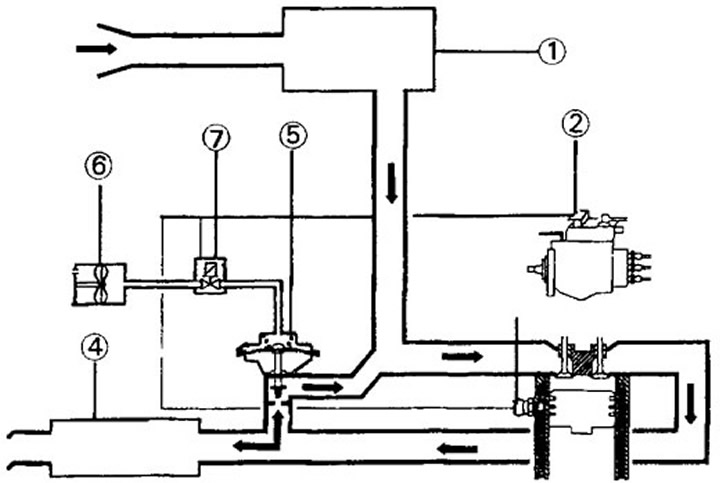
1.0b Exhaust gas recirculation system. 1.9 liter XUD9 engine with L3 emission standard
1 - air filter
2 - load sensor on high pressure fuel pump
3 - thermal switch at 60°C
4 - exhaust system
5 - mechanical exhaust gas valve
6 - vacuum pump
7 - EGR solenoid valve
Exhaust gas recirculation only takes place under certain conditions, depending on the coolant temperature and the engine load. The coolant temperature sensor in the outlet pipe provides the appropriate signal for the coolant temperature. Exhaust gas recirculation occurs when the engine reaches a temperature above 60°C, and the load on the engine does not exceed the nominal load value set in the load sensor attached to the high-pressure fuel pump. The control unit opens the EGR solenoid valve (7), which regulates the operation of the entire exhaust gas recirculation system (see illustration 1.0b). At the same time, the vacuum pressure generated by the vacuum pump located on the camshaft opens the mechanical exhaust gas valve installed on the exhaust manifold, and part of the exhaust gas is discharged into the intake manifold.
When the engine is running at low speeds, the low pressure generated by the vacuum pump reaches its maximum. The mechanical exhaust gas valve then remains open, diverting the exhaust gas to the intake manifold. Exhaust gas circulation is maintained by a pressure difference between the intake and exhaust manifolds, determined by the throttle valve, which closes almost completely.
As the engine accelerates and RPM increases, the low pressure generated by the vacuum pump drops and the mechanical exhaust gas valve is gradually closed by spring action, reducing the amount of exhaust gas sent to the intake manifold. At the same time, the throttle valve opens to let in more fresh air.
Coolant temperature sensor
This sensor is located in the coolant outlet pipe and informs the electronic control unit about the heating of the coolant above 60°C, which is a signal for opening the mechanical exhaust gas valve.
EGR solenoid valve
This valve is controlled by the ECM and supplies low pressure to the mechanical exhaust gas valve to the intake manifold.
Mechanical EGR valve
The mechanical exhaust gas valve is attached to the exhaust manifold and is designed to control the amount of exhaust gas re-discharged into the intake manifold for subsequent combustion. Under the influence of low pressure from the vacuum pump after the ECU opens the EGR solenoid valve to the mechanical valve diaphragm, the upper chamber of the mechanical valve opens. The valve is held in the closed position by a spring.
Fuel cut-off valve
The circuit of the fuel injection system includes a fuel cut-off solenoid valve that shuts off its supply when the ignition is turned off.
Safety sensor
To increase passive safety, cars are equipped with a safety sensor (switch), triggered in the event of a sudden forced stop of the car, as happens in a collision and turning off the fuel pump. The switch is located in the engine compartment above the battery. The switch can be returned to its working position by pressing its button.
Fuel injectors
The power supply system is equipped with fuel injectors of various types. The nozzles are color coded for easy recognition.
Preheating and tracking device
Preheating and maintenance function the same on all engines, however, some types of engines are not equipped with this device. The regulator that controls the operation of the preheating and maintenance device is located on the partition, below the battery. The regulator acts as a relay, from which power is supplied to the preheating candles. The glow plugs, as well as the control lamp of this device, are supplied with power at the moment the ignition is turned on, if the temperature of the coolant is below 60°C. After a while, the regulator cuts off the voltage supply to the pre-heating plugs. At the same time, in the phase of starting the engine, power is supplied to the candles and their glow continued for some time after the start.
Accompanying preheating means that the plugs continue to be in the glow phase after the engine is started. Accompaniment begins immediately after the engine is started and the starter is turned off. During the first 15 seconds, the voltage supply to the glow plugs cannot be interrupted. After 15 seconds, the power supply may turn off if the coolant temperature is above 60°C or if the accelerator pedal is in a certain position or is pressed for more than the programmed time.
Glow plugs
The type of glow plugs depends on the type of engine. The relevant data is given in the specifications.
Air filter
The air filter with a dry filter element is installed in the left side of the engine compartment on the inside of the wing. The purpose of the air filter is the same for all engines, but the filter itself may differ in shape. When purchasing a new filter element, it is necessary to indicate the letter designation of the filter, engine number and year of manufacture.
The filter element should be replaced according to the data in the service book (with a run of 60,000 km).
Exhaust gas recirculation system
All cars have an exhaust gas recirculation system, and an oxidizing type catalyst is installed only on certain models.
The exhaust gas recirculation system is designed to reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. Part of the exhaust gases through the recirculation valve is re-discharged into the intake manifold. Due to the fact that the exhaust gas contains a minimum amount of combustible gases, the re-intake of the exhaust gas lowers the temperature in the combustion chambers, thereby reducing the formation of nitrogen oxides.
Diesel fuel
Diesel fuel consists of so-called paraffins. This hydrocarbon substance is flammable, but crystallizes rapidly when the temperature is lowered. As a result, diesel fuel waxes and is unable to pass through the fuel filter. Diesel fuel manufacturers solve this problem by adding so-called fuel flow improvers. These additives are not able to prevent fuel crystallization when the ambient air temperature drops, but at the same time they retain its fluidity and fuel can be supplied to the injection pump.
When refueling, it is recommended to fill in diesel fuel with a cetane number of 45. This type of diesel fuel is all-weather.
Summer diesel fuel does not contain flow improvers. This fuel is paraffinized at temperatures below -2°C.
There is also the so-called «transitional» diesel fuel offered in spring and autumn. It withstands sub-zero temperatures ranging from -8°C to -10°C. ' '
Winter diesel fuel contains improving additives and crystallizes at temperatures of -22°C.
If the car has not been used for a long time, then it may happen that with the onset of cold weather it turned out to be filled with summer fuel. In this case, the problem that has arisen can be solved with the help of an appropriate additive-improver offered at gas stations. After choosing the type of additive you need, read the instructions for its use. After that, pour the contents, heated to room temperature, into the fuel tank and refuel to keep the tank full. Fuel at filling stations is stored in underground tanks and its temperature is sufficient for the additive to mix well with the fuel while driving.
This option is not possible if the summer fuel is waxed. In this case, the car should be put in a heated garage so that the fuel becomes fluid again. And only after that you can use the appropriate additive.
Reduced exhaust gas toxicity
Certain types of engines are equipped with an oxidation type catalyst (corresponds to unregulated catalyst). The catalyst reduces the emission of hydrocarbons and oxides by almost 50%. The catalyst is not a filter for soot and soot, but it helps to reduce their emissions. As a rule, gaseous hydrocarbons are usually retained by particulate soot, thereby increasing their volume in the exhaust gas. However, when using a catalyst, hydrocarbons are oxidized and cannot come into contact with carbon or soot particles.
