Gasoline-powered vehicles are equipped with a variable catalytic converter. Term «adjustable» indicates that the reduction of the content of harmful substances in the exhaust gas is achieved by adjusting the composition of the air-fuel mixture. For this purpose, an oxygen sensor is installed in the exhaust pipe in front of the catalyst (Lambda probe), which continuously monitors the oxygen level in the exhaust gas. Based on the data received from the lambda probe, the electronic control unit changes the composition of the air-fuel mixture, making it richer or leaner. Such a change in the composition of the air-fuel mixture occurs quite quickly and in the following sequence: an increase in the air supply for burning hydrocarbons, a decrease in the air supply (lack of air) to reduce the emission of nitrogen oxides. The gases formed during the combustion of the air-fuel mixture enter the catalyst, which almost completely converts them into carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide), steam and nitrogen.
Some models are not equipped with a catalyst.
The exhaust system of vehicles with a diesel engine is equipped with an oxidizing catalyst (unregulated catalyst). In this case, the catalyst reduces the emission of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide by almost 50%. The catalyst is not a filter that retains soot and other particles, but it also helps to reduce their content in the exhaust gas. Gaseous hydrocarbons settle on solid particles that form soot and, as a rule, carry them into the atmosphere. However, due to the fact that hydrocarbons are oxidized in the catalyst, they are unable to settle and combine with soot particles.
We do not recommend repairing a severely corroded exhaust pipe by welding it. The result of such work is rather meager, because after a while the pipe will have to be welded again. Putties and clamps are more effective in this case, however, after some time, the pipe begins to «crumble». As for the exhaust pipe with several mufflers, it often happens that immediately after replacing one muffler another one fails. For this reason, it is recommended to change both mufflers at once.
Workshops therefore change the exhaust system completely, which is not always justified. In each specific case, the condition of the exhaust system should be checked and a decision should be made whether to replace it completely or to replace only its individual parts.
When working on the exhaust system, the vehicle must be lifted and placed on jack stands. Make sure that the vehicle is firmly on the trestle and will not move when the exhaust pipes are removed.
If a connection is not released when the exhaust system is removed, it can be broken. When installing the exhaust gas system, be sure to replace all the fastening bolts and nuts with new ones.
The pipes of the system are separated by scrolling at the joints or knocked down with a hammer. If necessary, the pipe can be cut, stepping back about 10 cm from the junction. The rest of the pipe is cut lengthwise and disconnected with a large screwdriver.
All bolts of the exhaust system can be unscrewed more easily if the threads of the bolts were lubricated with copper grease when the system was installed. The same applies to the joints of the pipes of the system.
The exhaust system can be routed differently depending on the type of vehicle.
For vehicles with a gasoline engine, the exhaust system consists of three components: the front silencer pipe, the middle link with an additional silencer and the main silencer (see illustration 1.0).
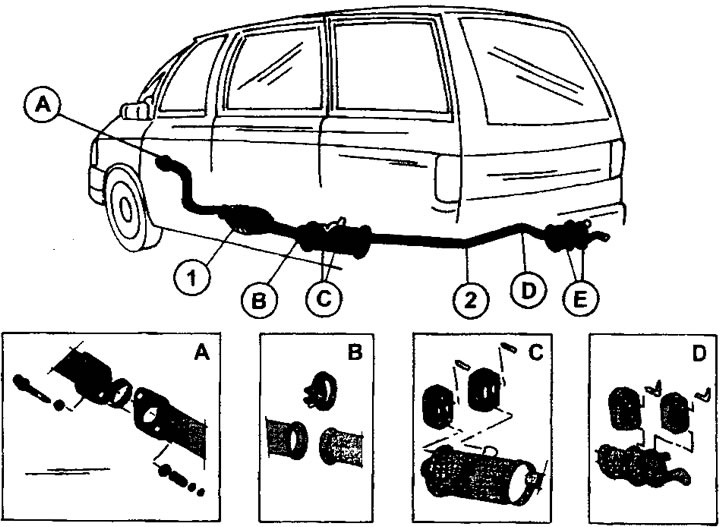
1.0 Exhaust system with catalytic converter
1 - catalyst
2 - front muffler pipe
A - catalyst mounting details
B - fastening the catalyst to the connecting pipe
С - fastening of the front part of the muffler
D - fastening of the rear part of the muffler
E - muffler connection
Attention! Not all vehicles are equipped with a catalytic converter.
Above the main and additional mufflers, under the fuel tank and the steering mechanism, heat-insulating shields are installed.
Exhaust systems usually differ in the design of the downpipe (see illustrations 1.0a, 1.0b, 1.0c and 1.0d).
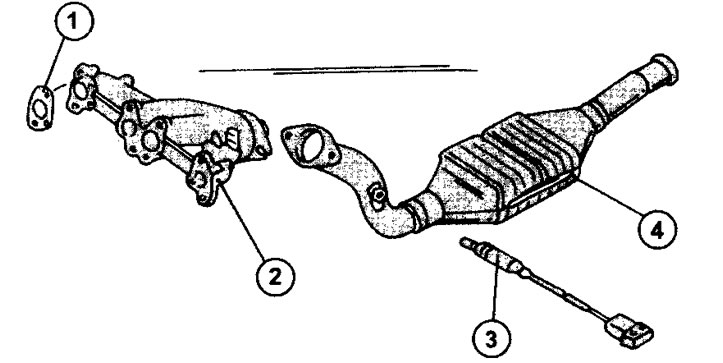
1.0a Downpipe for 1.8 and 2.0 liter XU engine mufflers without gas turbine supercharger.
1 - pipe gasket
2 - exhaust manifold
3 - lambda probe with wire and exhaust manifold plug
4 - catalyst
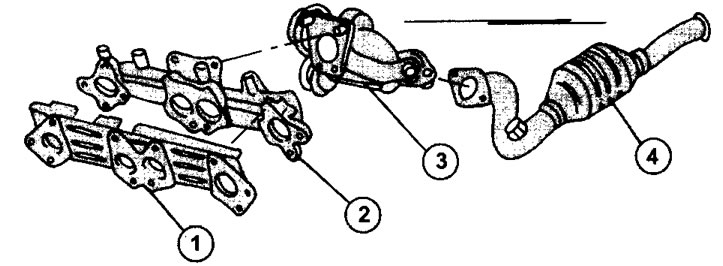
1.0b Downpipe for 2.0 liter XU engine mufflers with gas turbine supercharger.
1 - pipe gasket
2 - exhaust manifold
3 - gas turbine exhaust manifold supercharger
4 - catalyst
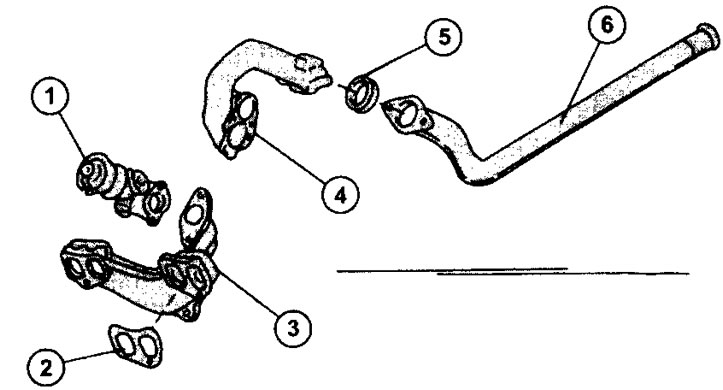
1.0v 1.9L XUD9 Diesel Muffler Downpipe
1 - EGR valve
2 - exhaust manifold pipe gasket
3 - exhaust manifold
4 - elbow of the exhaust pipe, attached to the turbocharger
5 - gasket
6 - front muffler pipe
The catalytic converter is not shown in this illustration because it is installed in an additional muffler or mounted on the front muffler pipe.
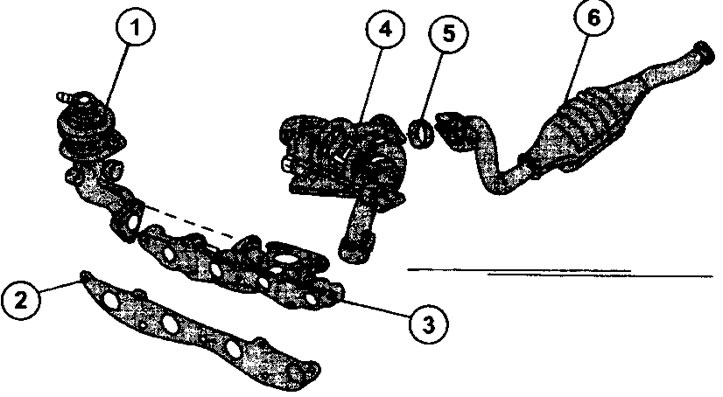
1.0g XUD11 2.1L Diesel Muffler Downpipe
1 - EGR valve
2 - pipe gasket
3 - exhaust manifold
4 - gas turbine supercharger
5 - exhaust manifold gasket
6 - oxidation type catalyst
