12.10 Intake air temperature sensor (ATS)
coolant temperature sensor (CTS) located in the cooling system and measures the engine coolant temperature.
Both sensors with negative temperature coefficient (NTC).
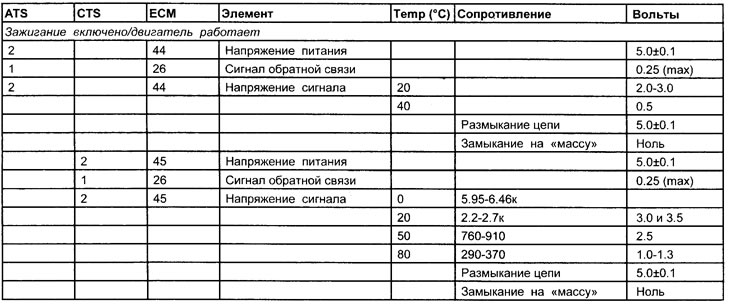
Voltage and resistance values of intake air temperature sensor and coolant temperature sensor
Terminal numbers
See illustration 12.11
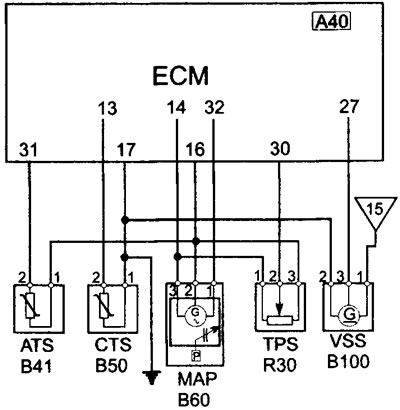
12.11 Wiring diagram ATS/CTS/MAP/TPS/VSS
Type of sensors
Both sensors with negative temperature coefficient (NTC)
Note. The intake air temperature sensor has little effect on engine operation.
Influence of external factors
- Vacuum leak
- Cooling system failure
- Low oil level
Checking sensors (general check)
1. If you suspect a malfunction of any of the sensors, you must perform the following checks.
2. Inspect the multi-pin connector for signs of corrosion and damage.
3. Make sure the connector terminal pins are properly installed and making good contact with the multi-pin connector.
Checking the performance of sensors with an oscilloscope or voltmeter
1. Bend the rubber insulation to the multi-pin connectors (where possible) or connect output unit (WWII) between the multi-pin connector of the electronic control unit and the electronic control unit.
2. Connect the negative lead of the oscilloscope or voltmeter to ground on the motor OR to ground on the sensor.
3. Connect the positive probe of an oscilloscope or voltmeter to the sensor's signal wire terminal.
4. The engine is not running, the ignition is on.
Checking the intake air temperature sensor (ATS)
1. The signal voltage will change according to the intake air temperature or coolant temperature. See diagram showing voltages at various temperatures.
2. When testing at different temperatures, the intake air temperature sensor (ATS) can be heated with a hair dryer or cooled with something like «Freezit», which is a cooling aerosol spray that can be purchased at electrical stores. When the intake air temperature sensor heats up or cools down, the temperature changes, so the resistance and voltage change accordingly.
3. If the signal voltage of the intake air temperature sensor is zero (open circuit or short to «mass») or 5.0 Volts (ATS - open circuit), then perform the appropriate checks as described below.
Checks with the engine running (CTS)
1. Let the engine cool down.
2. The engine is not running, the ignition is on.
3. The signal voltage will change according to the temperature. See the coolant temperature sensor diagram for voltages at various temperatures.
4. Verify that the voltage of the coolant temperature sensor matches the temperature of the coolant temperature sensor.
5. Start the engine and let it warm up to normal operating temperature. With the engine warm, the voltage should decrease according to the coolant temperature sensor circuitry.
6. The main problem is that the readings of the coolant temperature sensor (CTS) resistance (and stress) outside the normal ranges.
The coolant temperature sensor voltage can typically be between 3.0 and 3.5 volts when the engine is cold and between 1.0 and 1.3 volts when the engine is warm. If the voltage changes from 1.75 volts on a cold engine to 1.25 volts on a warm engine, the engine will be difficult to start from a cold state, and running a warm engine on a too rich fuel mixture will be difficult.
- The self-diagnosis system will not generate a DTC because the coolant temperature sensor is still operating within its design parameters. 7 If the signal voltage of the coolant temperature sensor is zero (opening of the supply circuit or short circuit to «mass») or 5.0 Volts (CTS - open circuit), then perform the appropriate checks described below
Zero Volts at signal wire terminal
1. Check if the signal wire is shorted «to ground».
2. Check for continuity in the signal wire between the sensor and the electronic control unit.
3. If the wiring of the coolant temperature sensor is OK, then check the power and ground contacts of the electronic control unit. If the contacts are in order, then the electronic control unit may be faulty.
5.0 volts at signal wire terminal
1. This voltage indicates that the circuit is open. This can be caused by the following:
2. The signal wire terminal in the sensor's multi-pin connector is not making good contact with the sensor.
3. Open circuit of the sensor or signal wire of the sensor.
4. Breakage of the grounding part of the sensor circuit.
The signal voltage or supply voltage matches the battery voltage
- Check for a short in the wire connected to the positive terminal (+) battery, or the supply circuit of the sensor.
Resistance checks with an ohmmeter
Intake air temperature sensor
- The resistance detection test can be performed at various temperatures as well as by comparison made with a temperature/resistance circuit. Familiarize yourself with the voltage test using the heating/cooling method of the coolant temperature sensor.
The coolant temperature sensor is installed on the vehicle
- The resistance detection test can be performed at various temperatures as well as by comparison made with a temperature/resistance circuit. When the resistance is within the specified parameters for a cold engine (20°С), the coolant temperature must be within±5°C of this figure.
Note. If during testing the temperature was measured by applying a thermometer to the outside of the coolant channel or coolant temperature sensor, then it must be taken into account that the actual coolant temperature may be slightly higher than the surface temperature of the coolant temperature sensor.
Coolant temperature sensor removed from vehicle
1. The recommended method is to remove the coolant temperature sensor from the vehicle.
2. Place the sensor in a suitable container of water and measure the temperature of the water.
3. Measure the resistance of the coolant temperature sensor and check the resistance against the table.
4. Heat the water by periodically measuring the water temperature and the resistance of the coolant temperature sensor, and compare the resistance values with the data given in the table.
