Ignition coil
The ignition coil uses low resistance on the primary side of the ignition coil to increase primary current and primary energy. The amplifier limits the current in the primary winding to approximately 8 A in order to accumulate the necessary energy reserve to create a spark discharge.
Static ignition system
Although the ignition system is referred to as a static ignition system, its basic functions are the same as on models equipped with a conventional non-contact ignition system. In static (without distributor) ignition system (DIS) or the so-called «idle spark system» two ignition coils are used to create a spark discharge on two spark plugs at the same time (see illustration 12.8).
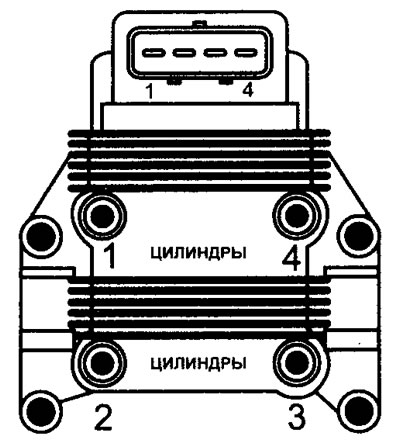
12.8 Static ignition coil (DIS)
One cylinder creates a spark discharge on the compression stroke, and a paired cylinder - on the exhaust stroke, where the spark does not perform any useful function, i.e. is «idle».
Therefore, two pairs of ignition coils are required for a 4-cylinder engine. Approximately 3 kV is still needed to create «idle spark». Each ignition coil receives voltage from the ignition switch, as well as from a separate wire going to the electronic control unit. Thus, the electronic control unit can turn on each ignition coil individually.
Voltage values in the primary winding of the ignition coil
Note. Voltage is supplied by the fuel pump relay and is only available for approximately one second after the ignition is turned on - either when cranking or with the engine running. Bypassing the relay ensures that the voltage needed for the test is supplied when the engine is off.
Terminal numbers
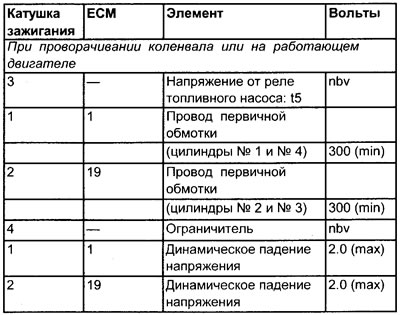
See illustration 12.6
Checking the primary winding of the ignition coil (general check)
1. Check up reliability of connection of plugs of the coil of ignition.
2. Clean accumulated dirt and deposits from the ignition coil pack using an aerosol. The remaining dirt contributes to the formation of new dirt, which often leads to leakage currents.
3. Inspect ignition coil for excessive leaks (current), especially around the spool pin.
4. Connect the negative lead of an oscilloscope or breaker closed time meter to ground on the motor.
5. Connect the positive lead of an oscilloscope or breaker closed time meter to the negative terminal (-) one of the two ignition coils #1 or #2.
6. After checking one terminal of the ignition coil, perform a test on the other terminal.
Checks with the engine off
1. Turn the crankshaft.
2. Either the waveform of the primary winding or duty cycle indication must be obtained. If the device can measure readings in milliseconds, then this is the most successful measurement.
Oscilloscope
In addition to a clear waveform, peak voltages in the primary must be at least 300 volts.
3. Clear primary waveform or sufficient signal:
- Primary winding of the ignition coil (including crank angle sensor (CAS)) gives a sufficient signal.
- The fault is not related to the low voltage circuit of the ignition system.
4. Fuzzy primary waveform or weak signal:
- Check the signal from the crankshaft angle sensor.
5. Connect the positive probe of an oscilloscope or voltmeter to the ignition coil #3 terminals.
6. Turn the crankshaft and check for voltage on the positive (+) ignition coil terminal No. 3.
7. If there is no voltage, trace the wiring back to the supply terminal of the relay.
8. Check for voltage on the negative (-) terminals of ignition coils No. 1 and No. 2.
9. If there is no voltage, disconnect the wire from the terminal (-) ignition coils and check again.
10. If, as before, there is no voltage, check the resistance on the primary winding of the ignition coil.
11. The voltage corresponds to the rated voltage of the battery, check for a short to «mass» between the corresponding terminal of the ignition coil and the contact pin of the electronic control unit.
12. Disconnect the multi-pin connector of the electronic control unit and check the presence of battery voltage at terminals No. 1 and No. 19 of the electronic control unit while cranking the crankshaft.
13. Weak voltage or no voltage:
- Check for continuity between the ignition coil terminal and the ECU pin.
14. If the wiring is in order, check all power and ground contacts of the electronic control unit.
15. If the checks did not find any malfunctions, then the electronic control unit may have failed. However, before replacing the electronic control unit, the replacement ignition coil should be checked.
Checks with the engine running
1. Perform the following checks on the primary terminal of ignition coil #1 and then in turn on coil #2. The results at each terminal should be very similar.
2. Connect an oscilloscope or breaker closed time meter to the negative terminal of ignition coil #1.
3. Start the engine and let it run at idle and at various speeds. Record duty cycle, peak primary voltage, and dynamic voltage drop.
4. Compare your results with the values given in the specifications. Keep in mind that duty cycle readings vary between different vehicles of the same model. However, ms readings should be as accurate as possible.
5. It is important that as the engine speed increases, the percentage of duty cycle (%) increased.
6. It is important that as the engine speed increases, the values of the duty cycle in msec do not differ too much.
7. If the dynamic voltage drop is high (typically over 2.5 volts) coupled with low peak voltage in the primary winding and high pulse expansion % (idle), then you should check the performance of the amplifier.
Warning. If the dynamic voltage drop is high (typically over 2.5 volts), but the peak value of the voltage in the primary winding and the expansion of the pulses% is normal, then the amplifier may be working. Keep in mind that the amplifier is an integral part of the ECU on this model, so readings will not improve when you replace the ECU just because the dynamic voltage drop is too high.
Checking the electronic control unit
1. Check the ground contacts of the electronic control unit.
2. Make sure that wires from devices such as a radio interference suppressor or burglar alarm systems are not connected to the terminal (-) primary winding of the ignition coil.
3. If the ground and wires are normal, and the peak value of the primary voltage and the expansion of the pulses% in idle mode is very high, then the electronic control unit is definitely defective. Read the warning above before replacing the electronic control unit.
4. The results obtained at each terminal should be very similar.
