Share information:
Bosch Motronic MP 3.2 engine management system Peugeot 806
General description
Electronic engine management system (EMS) Bosch Motronic MP3.2, which has been used to control Citroen and Peugeot engines since around 1993, is an integrated system that controls ignition coil primary, fuel delivery...
Electronic engine management system (EMS) Bosch Motronic MP3.2, which has been used to control Citroen and Peugeot engines since around 1993, is an integrated system that controls ignition coil primary, fuel delivery...
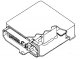
Checking the electronic control unit ECM (general check)
Checking the electronic control unit ECM (general check) 1. Inspect the multi-pin connector of the electronic control unit for signs of corrosion and damage. 2. Make sure that the connector terminal pins are properly...
Checking the electronic control unit ECM (general check) 1. Inspect the multi-pin connector of the electronic control unit for signs of corrosion and damage. 2. Make sure that the connector terminal pins are properly...
Self-diagnosis function
The Bosch Motronic MP3.2 system has the ability to self-test, which consists in the continuous evaluation of the signals received from the sensors, and in the event of a malfunction, it enters the appropriate code into...
The Bosch Motronic MP3.2 system has the ability to self-test, which consists in the continuous evaluation of the signals received from the sensors, and in the event of a malfunction, it enters the appropriate code into...
Ignition systems
Bosch Motronic MP3.2 uses two types of ignition coils: or static (without distributor) ignition system or direct ignition (DI). Static (without distributor) ignition system (DIS) Although the ignition system is referred...
Bosch Motronic MP3.2 uses two types of ignition coils: or static (without distributor) ignition system or direct ignition (DI). Static (without distributor) ignition system (DIS) Although the ignition system is referred...
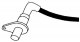
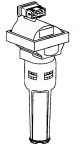
Crank Angle Sensor (CAS)
crank angle sensor (CAS), which determines the fuel injection time and ignition timing, is located next to the flywheel (see illustration 11.9). The crank angle sensor consists of an inductive magnet that emits a...
crank angle sensor (CAS), which determines the fuel injection time and ignition timing, is located next to the flywheel (see illustration 11.9). The crank angle sensor consists of an inductive magnet that emits a...
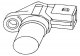
Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP)
Camshaft position sensor (SMR) determines the position of the #1 piston in its cylinder for sequential fuel injection signals to each cylinder. In the MP3.2 system, this sensor is a Hall sensor to produce a signal....
Camshaft position sensor (SMR) determines the position of the #1 piston in its cylinder for sequential fuel injection signals to each cylinder. In the MP3.2 system, this sensor is a Hall sensor to produce a signal....
Ignition booster
Ignition booster (see illustration 11.15) includes a circuit to connect the negative terminal of the ignition coil to create a spark discharge. Depending on the model, either one or two separate amplifiers are used in...
Ignition booster (see illustration 11.15) includes a circuit to connect the negative terminal of the ignition coil to create a spark discharge. Depending on the model, either one or two separate amplifiers are used in...
Ignition Coil Static Ignition System (DIS)
Although the ignition system is referred to as a static ignition system, its basic functions are the same as on models equipped with a conventional non-contact ignition system. In static (without distributor) ignition...
Although the ignition system is referred to as a static ignition system, its basic functions are the same as on models equipped with a conventional non-contact ignition system. In static (without distributor) ignition...
Ignition coils for direct ignition systems
Ignition coils (see illustration 11.19) use low resistance on the primary side of the ignition coil to increase primary current and primary energy. The amplifier limits the current in the primary winding to...
Ignition coils (see illustration 11.19) use low resistance on the primary side of the ignition coil to increase primary current and primary energy. The amplifier limits the current in the primary winding to...
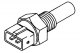
Intake air temperature sensor and coolant temperature sensor (ATS and CTS)
intake air temperature sensor (ATS) (see illustration 11.20) located in the air intake where it measures the temperature of the air drawn into the engine. The signal from the ATS sensor makes it possible to more...
intake air temperature sensor (ATS) (see illustration 11.20) located in the air intake where it measures the temperature of the air drawn into the engine. The signal from the ATS sensor makes it possible to more...
Knock sensor (KS)
Since knocking can occur at different times in each individual cylinder, Bosch Motronic MP3.2 uses a knock control unit - KCU (in the electronic control unit), to indicate the specific cylinder or cylinders where...
Since knocking can occur at different times in each individual cylinder, Bosch Motronic MP3.2 uses a knock control unit - KCU (in the electronic control unit), to indicate the specific cylinder or cylinders where...
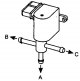
Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor
The main engine load sensor is the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor. Vacuum hose connects the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor (located in the electronic control unit) (see illustration 5.1) and intake...
The main engine load sensor is the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor. Vacuum hose connects the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor (located in the electronic control unit) (see illustration 5.1) and intake...
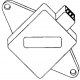
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
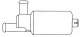
Throttle position sensor (TPS) (see illustration 11.26) used to inform the ECU of throttle position and acceleration rate. The MP3.2 ECU uses the signal from the throttle position sensor to determine engine idle,...
Throttle position sensor (TPS) (see illustration 11.26) used to inform the ECU of throttle position and acceleration rate. The MP3.2 ECU uses the signal from the throttle position sensor to determine engine idle,...
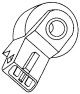
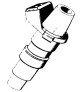
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
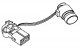
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) (see illustration 11.28) used to notify the ECU of vehicle speed. This sensor is a Hall effect sensor and is located directly on the gearbox. Voltage is supplied to the vehicle speed sensor...
Vehicle speed sensor (VSS) (see illustration 11.28) used to notify the ECU of vehicle speed. This sensor is a Hall effect sensor and is located directly on the gearbox. Voltage is supplied to the vehicle speed sensor...
Induction Changeover Valve (ICOV) (non-turbocharged models only)
Under all operating conditions, air enters the intake manifold through the throttle valve into the throttle body. However, on Citroen and Peugeot vehicles equipped with the Bosch Motronic MP3.2, an induction changeover...
Under all operating conditions, air enters the intake manifold through the throttle valve into the throttle body. However, on Citroen and Peugeot vehicles equipped with the Bosch Motronic MP3.2, an induction changeover...
Idle Air Control Valve (ISCV)
Idle control valve (1SCV) (see illustration 11.32) used by the Bosch Motronic MP3.2 ECU to automatically control the idle speed at normal idle and while the engine is warming up. The idle air control valve is located in...
Idle control valve (1SCV) (see illustration 11.32) used by the Bosch Motronic MP3.2 ECU to automatically control the idle speed at normal idle and while the engine is warming up. The idle air control valve is located in...
Intake manifold heater (IMH)
intake manifold heater (IMH) (see illustration 11.34) designed to heat the throttle body so that it does not freeze in cold weather. When the engine is running, the heater is on all the time. PTC Heater (RTS) allows the...
intake manifold heater (IMH) (see illustration 11.34) designed to heat the throttle body so that it does not freeze in cold weather. When the engine is running, the heater is on all the time. PTC Heater (RTS) allows the...
Turbocharger Wastegate (WCS) (only with turbocharger)
The turbocharger is located in the exhaust system close enough to the exhaust manifold. Boost control (models equipped with a turbocharger) When the volume of exhaust gases increases, the turbocharger starts to work...
The turbocharger is located in the exhaust system close enough to the exhaust manifold. Boost control (models equipped with a turbocharger) When the volume of exhaust gases increases, the turbocharger starts to work...
Fuel injection system
The Bosch Motronic electronic control unit determines the moment and duration of injector opening depending on engine speed and engine load. This information is fed to the ECU from various sensors, such as the intake...
The Bosch Motronic electronic control unit determines the moment and duration of injector opening depending on engine speed and engine load. This information is fed to the ECU from various sensors, such as the intake...
Fuel system
The fuel pump typically delivers much more fuel than needed and the excess fuel is returned to the fuel tank through the return line. In fact, the maximum allowable fuel pressure of more than 4 bar is possible in this...
The fuel pump typically delivers much more fuel than needed and the excess fuel is returned to the fuel tank through the return line. In fact, the maximum allowable fuel pressure of more than 4 bar is possible in this...
Fuel pump
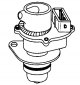
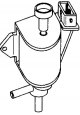
Models equipped with the Motronic MP3.2 system can be equipped with a fuel pump mounted inside the fuel tank or outside next to the fuel tank. Fuel pump located outside next to the fuel tank (see illustration 5.39). The...
Models equipped with the Motronic MP3.2 system can be equipped with a fuel pump mounted inside the fuel tank or outside next to the fuel tank. Fuel pump located outside next to the fuel tank (see illustration 5.39). The...
Fuel pressure control
The fuel pressure regulator constantly maintains the fuel pressure in the fuel line at 3.0 bar. The fuel pressure regulator is installed on the fuel line and consists of two chambers separated by a diaphragm. The upper...
The fuel pressure regulator constantly maintains the fuel pressure in the fuel line at 3.0 bar. The fuel pressure regulator is installed on the fuel line and consists of two chambers separated by a diaphragm. The upper...
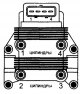
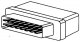
Fuel pump relay
Main relay and fuel pump relay (single double contact relay) The Bosch Motronic electrical system is controlled by a single 15-pin double contact relay (see illustration 11.41 and 11.42). The supply of constant voltage...
Main relay and fuel pump relay (single double contact relay) The Bosch Motronic electrical system is controlled by a single 15-pin double contact relay (see illustration 11.41 and 11.42). The supply of constant voltage...
Catalytic Converter and Emission Control System
All versions of the Bosch Motronic MP3.2 fuel injection system are equipped with a catalytic converter and have a closed loop system, so that harmful exhaust emissions can be minimized. Closed loop systems are equipped...
All versions of the Bosch Motronic MP3.2 fuel injection system are equipped with a catalytic converter and have a closed loop system, so that harmful exhaust emissions can be minimized. Closed loop systems are equipped...
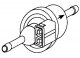
Oxygen sensor (OS)
Oxygen sensor closed loop voltage (OS) (see illustration 11.44) is quite low, ranging from 100 mV to 1.0 V. The signal frequency is approximately 1 Hz. A digital voltmeter connected to the signal wire will indicate an...
Oxygen sensor closed loop voltage (OS) (see illustration 11.44) is quite low, ranging from 100 mV to 1.0 V. The signal frequency is approximately 1 Hz. A digital voltmeter connected to the signal wire will indicate an...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Link to this section in different formats
TEXTHTMLBB Code
- General information
- Introduction to the guide
- Faults en route
- Weekly checks
- User manual
- Maintenance (petrol)
- Maintenance (diesel)
- Power unit
- Petrol engines
- Diesel engines «XUD»
- Diesel engines «DW»
- Overhaul of petrol engines
- Overhaul of diesel engines
- Cooling and heating
- Power and exhaust (petrol)
- Power and exhaust (XUD diesels)
- Power and exhaust (DW diesels)
- Emission reduction
- Starting and charging system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis, running gear
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body and interior
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines
- Diesel engines
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Fuel injection (petrol)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Ignition and exhaust systems
- ECM Bosch Motronic MP 3.2
- ECM Magneti-Marelli (MM)
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Chassis, running gear
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits