11.44 Oxygen sensor (OS)
The closed-loop oxygen sensor signal causes the electronic control unit to change the injector stroke in such a way that the composition of the air-fuel mixture is kept as close to the stoichiometric ratio as possible. By controlling the fuel injection stroke, under most operating conditions, so that the air-fuel ratio is always within a small window around the Lambda point (i.e. Lambda = 0.981.04), at which almost complete combustion is achieved.
The oxygen sensor operates in closed loop when the engine is warmed up to normal operating temperature. If the coolant temperature is below 70°C or the engine load is at or above normal, the ECU will operate in open loop. When operating in open loop, the electronic control unit adjusts the air-fuel mixture, making it richer or leaner than required for the stoichiometric ratio. This prevents erratic engine operation, such as when accelerating at wide open throttle.
In order for the oxygen sensor to reach its maximum operating temperature as quickly as possible after starting the engine, it contains a heating element.
The supply voltage to the oxygen sensor heater comes from terminal No. 9 of the main relay (fuel pump) (only for models 306) or to terminal no. 1 (ignition coil and intake manifold heater) (for all other models). Terminals #1 and #9 are grouped together in a relay. Therefore, the oxygen sensor heater will only function when the engine is running.
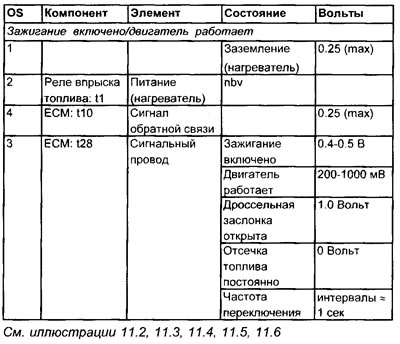
Oxygen Sensor Voltage Values (OS)
Terminal numbers
Influence of external factors
- Poor oxygen sensor ground
- Dirty oxygen sensor
- Vacuum leaks
- Malfunction of the ignition system or fuel system
- Oil thinning
- Clogged air filter
- Leaded gasoline
- Low fuel pressure
- Exhaust leaks (master oxygen sensor)
Checking the signal from the oxygen sensor
1. Connect the negative lead of an oscilloscope or voltmeter to ground on the motor.
2. Connect the positive probe of an oscilloscope or voltmeter to terminal No. 3 of the signal wire of the oxygen sensor.
3. If possible, connect a gas analyzer to the exhaust gas system that determines the content of 4 gases and the parameter «lambda».
4. The gas analyzer should show the following values:
- CO: as indicated in the specifications
- HC: less than 50 ppm
- SO2: over 15.0
- ABOUT2: less than 2.0
- Lambda: 1.0±0.04
Switching the oxygen sensor
1. Ignition on: the gauge should show 0.5 volts.
2. If there is no voltage, check the continuity of the wiring back to the signal wire terminal of the electronic control unit.
3. Start the engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
4. Increase engine speed to 3000 rpm for 30 seconds. Under this condition, the temperature of the oxygen sensor will rise enough for the switchover to occur.
5. Maintain engine speed - 2000 rpm. If the engine is left idling for a long time, the oxygen sensor will cool down and shifting may stop.
6. The voltage will change from about 0.8 volts (800 mV) up to 0.2 Volt (200 mV).
7. The digital voltmeter will indicate an average voltage of approximately 0.45 volts (450 mV).
8. Switching frequency - approximately 1 Hz (i.e. one pulse per second).
9. If the oscilloscope can set the time base to more than one second, then a sinusoidal switching waveform can be obtained (see illustration 11.45).
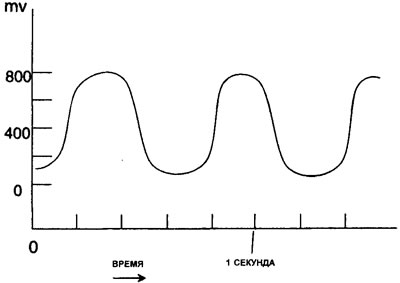
11.45 Oxygen sensor typical output (OS)
10. If the voltage reading is mainly between 0.6 V and 1.0 V, then the gases in the exhaust pipe have a small amount of oxygen, indicating a rich mixture (see illustration 11.46).
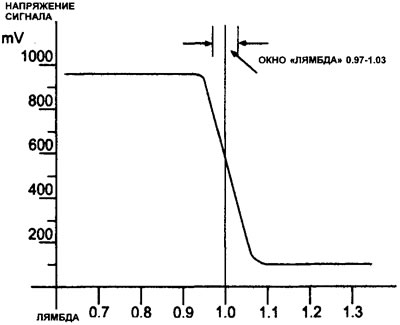
11.46 Typical output voltage vs «lambda»
11. If the voltage is mainly between 0.2 V and 0.6 V, then the gases in the exhaust pipe have too much oxygen. This may indicate one of the following conditions:
- Vacuum leak
- lean mixture
- Misfire
- Mechanical failure
- Ignition system malfunction
- Exhaust leak (in front of the oxygen sensor (OS)
- Slow switching (much more than 1 hertz) may indicate contamination of the oxygen sensor.
Oxygen Sensor Heater Tests
1. Check for battery voltage at terminal #2 of the oxygen sensor.
2. If there is no voltage, trace the supply wiring back to the relay or ignition switch (depending on system device).
3. Check the ground connection of the oxygen sensor heater.
