2. Lay out piston assemblies with connecting rods and new sets of piston rings in such a way that both when measuring gaps in the ring locks and when reassembling the engine, the sets of rings always correspond to the same piston and cylinder.
3. Insert the top ring into the first cylinder and press it into the cylinder using the piston head as a mandrel. This will force the ring to be perpendicular to the walls of the cylinder. Position the ring near the base of the cylinder, at the lower end of the ring travel zone. Keep in mind that the top and second compression rings are different from each other. The second ring can be identified by its cone; in addition, it has a step on the bottom surface.
4. Measure the gap in the lock of the ring with «fan» probe.
5. Repeat the procedure with this ring in the upper zone of the cylinder, at the upper limit of its movement (pic. 16.5) and compare the measurement results with the values given in «Specifications». If the joint clearances are incorrect, check that the rings are correctly selected for the specific engine and for the given cylinder size.
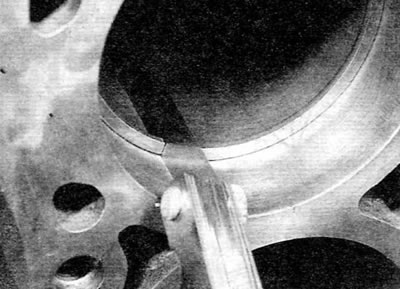
Pic. 16.5. Measure the piston ring gaps with «fan» probe
6. Repeat the procedure for checking each ring in the first cylinder and do the same for the rings in the remaining cylinders. Don't forget to keep the rings, pistons and cylinders aligned.
7. After checking the gaps in the locks, the rings can be installed on the pistons.
8. First install the oil ring expansion element, and then install the ring.
9. The lower and upper compression rings are different and can be recognized by their cross section. The top ring is symmetrical, while the second ring is tapered. Install the second ring so that the identification mark (TOR) was facing up, and then install the top ring (pic. 16.9). Rotate the rings so that the locks are at an angle of 120°to each other. Note. Be sure to follow the instructions that come with new piston ring kits. Different manufacturers may prescribe different procedures. Do not confuse the top and second compression rings as they have different cross sections.
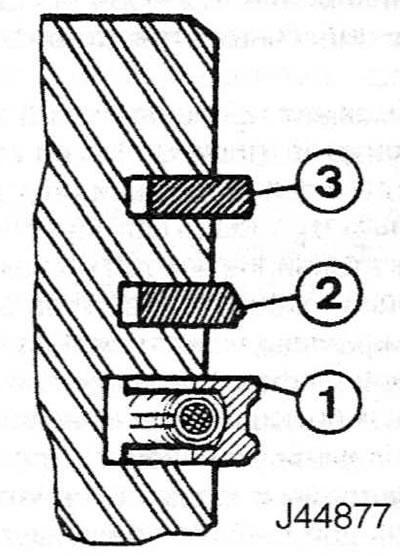
Pic. 16.9. Typical Piston Ring Arrangement
1. Oil scraper ring
2. Second compression ring
3. Top compression ring
